JVM Warm-Up Optimization for Ultra-Fast Startup in Spring Boot
Views: 0

Achieving fast application startup is critical for modern cloud deployments. JVM Warm-Up Optimization plays a crucial role in speeding up Spring Boot applications by reducing cold start delays. In this article, we’ll dive deep into how effective JVM Warm-Up Optimization techniques can help you launch your Spring Boot services faster and more efficiently.
Why JVM Warm-Up Matters in 2024+
Bob just deployed his Spring Boot microservice to Kubernetes.
It starts… slowly. The cold start time is 4–8 seconds, causing:
- Slow scale-out under load
- Wasted time on cloud functions
- CI tests that take forever
Bob wants his JVM to behave like a warmed-up engine — ready to race instantly.
Let’s explore how to optimize Spring Boot startup performance using JVM warm-up strategies
The Problem: JVM Isn’t Fast Cold
The JVM uses JIT (Just-In-Time) compilation, which optimizes bytecode after the app starts.
This means:
- Cold starts run in interpreted mode = slower
- Hot paths get faster later
- Warm-up can take 5–30 seconds for real apps
Optimization Strategy Overview

1. Enable Class Data Sharing (CDS)
CDS stores pre-processed class metadata in a shared archive.
Create archive:
java -Xshare:dumpUse archive:
java -Xshare:on -jar myapp.jar✔ Cuts classloading time by 10–30%
✔ Built-in for JDK 12+
2. Use AppCDS (Application-Specific)
AppCDS preloads specific classes for your app.
Create AppCDS archive:
java -Xshare:off -XX:DumpLoadedClassList=classes.lst -jar myapp.jar
java -XX:SharedClassListFile=classes.lst -XX:SharedArchiveFile=app-cds.jsa -Xshare:dumpRun:
java -XX:SharedArchiveFile=app-cds.jsa -Xshare:on -jar myapp.jar✔ Better for big apps like Spring Boot
✔ Reduces cold start time by 20–40%
3. Spring Boot Layer Index Optimization
Spring Boot 2.3+ adds a layers.idx that lets Docker layers load in order.
Add to Dockerfile:
FROM openjdk:21
ADD target/demo.jar app.jar
RUN java -Djarmode=layertools -jar app.jar extract✔ Speeds up container boot
✔ Great for cloud-native deployments
4. JIT Warm-Up with Profile-Based Optimization

Use JITCompiler logs to simulate production load, then recompile:
Enable profiling:
-XX:+UnlockDiagnosticVMOptions -XX:+LogCompilation
Use a load script to hit endpoints:
curl http://localhost:8080/api/test
Then restart the app with that profile.
✔ Helps pre-JIT key methods
✔ Ideal for CI/CD and startup benchmarks
5. AOT Compilation (Spring Boot Native / GraalVM)

Want real cold starts <100ms?
✔ Spring Boot + GraalVM native-image
This compiles the entire app to native code, skipping the JVM warm-up altogether.
Spring Boot Native Example:
spring-native-image -cp app.jar -o myapp
Result:
- Startup time: ~20–80ms
- Memory: ~40% less
- Instant warm-up!
Benchmarks — Before vs After (Spring Boot REST API)
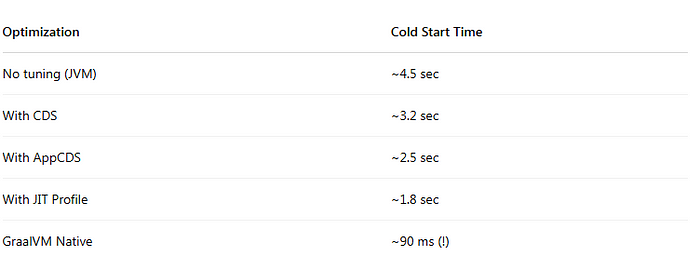
Summary: What Bob Should Do

Find us
linkedin Shant Khayalian
Facebook Balian’s
X-platform Balian’s
web Balian’s
Youtube Balian’s
#jvm #springboot #startupoptimization #graalvm #javaperformance #microservices #cloudnative #appcds #nativeimage #java21